Transcribed ultraconserved regions (T-UCRs) associated with cancer

Download scientific diagram | -Transcribed ultraconserved regions (T-UCRs) associated with cancer cell processes. They mostly affect cell proliferation, migration/invasion and apoptosis in distinct tumor types. Green arrows meaning promotion and red arrows meaning suppression of the mechanisms. Created with BioRender.com from publication: Transcribed Ultraconserved Regions: New regulators in cancer signaling and potential biomarkers | The ultraconserved regions (UCRs) are 481 genomic elements, longer than 200 bp, 100% conserved in human, mouse, and rat genomes. Usually, coding regions are more conserved, but more than 80% of UCRs are either intergenic or intronic, and many of them produce long non-coding | Transcribing, Prognosis and Regulations | ResearchGate, the professional network for scientists.
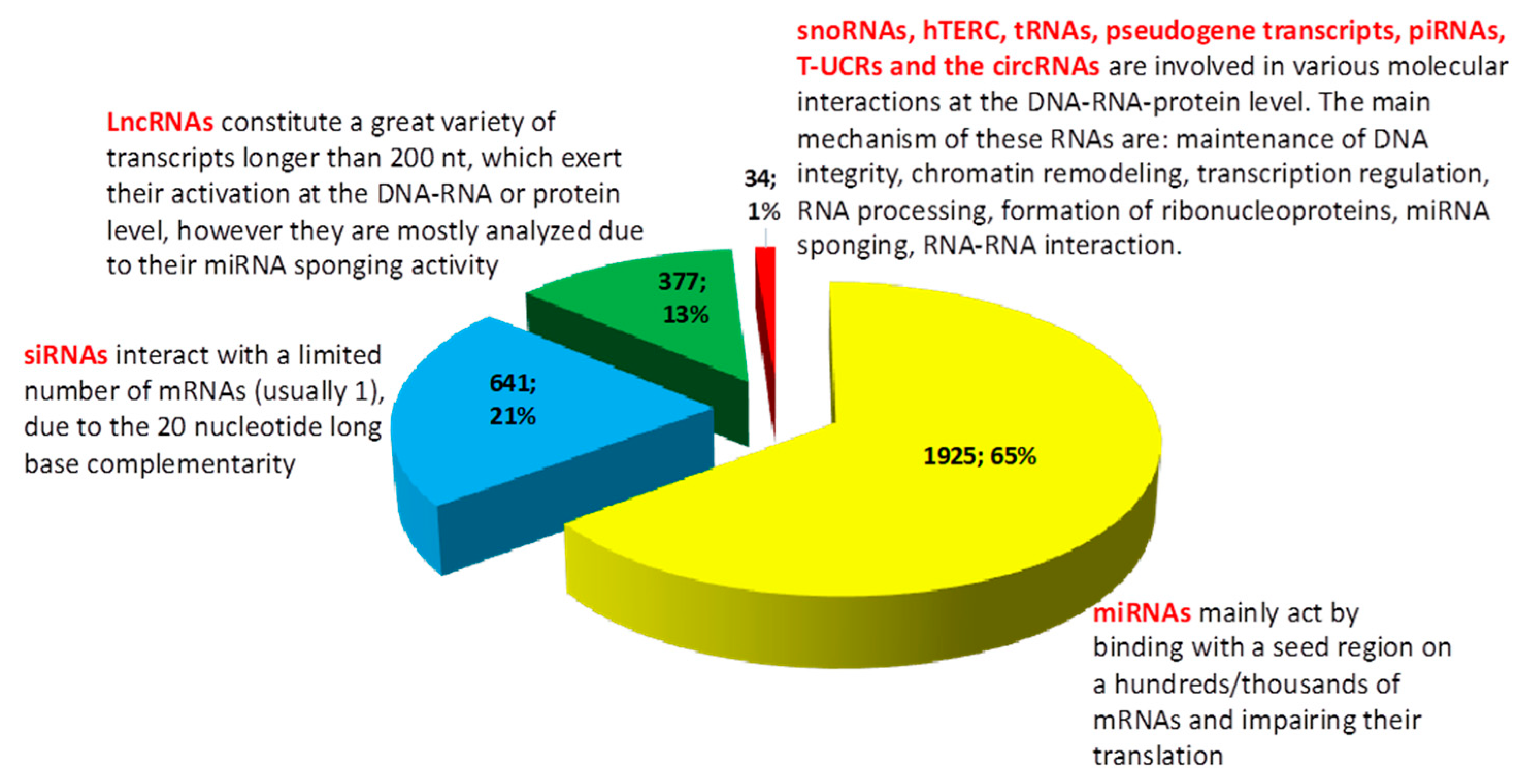
Cancers, Free Full-Text
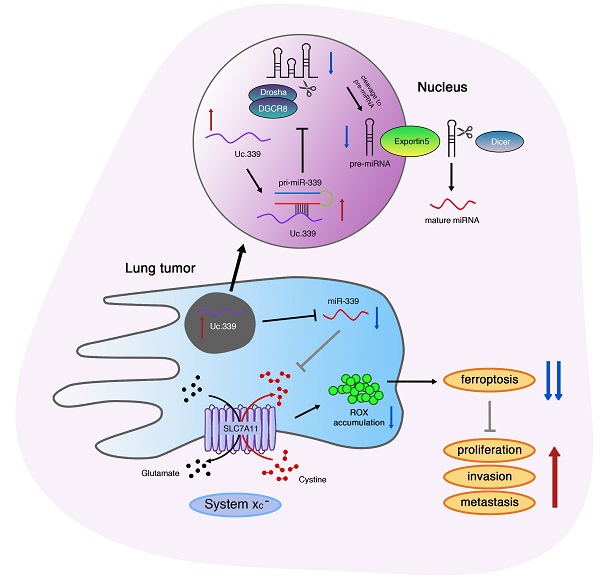
LncRNA T-UCR Uc.339/miR-339/SLC7A11 Axis Regulates the Metastasis of Ferroptosis-Induced Lung Adenocarcinoma

Biomolecules, Free Full-Text
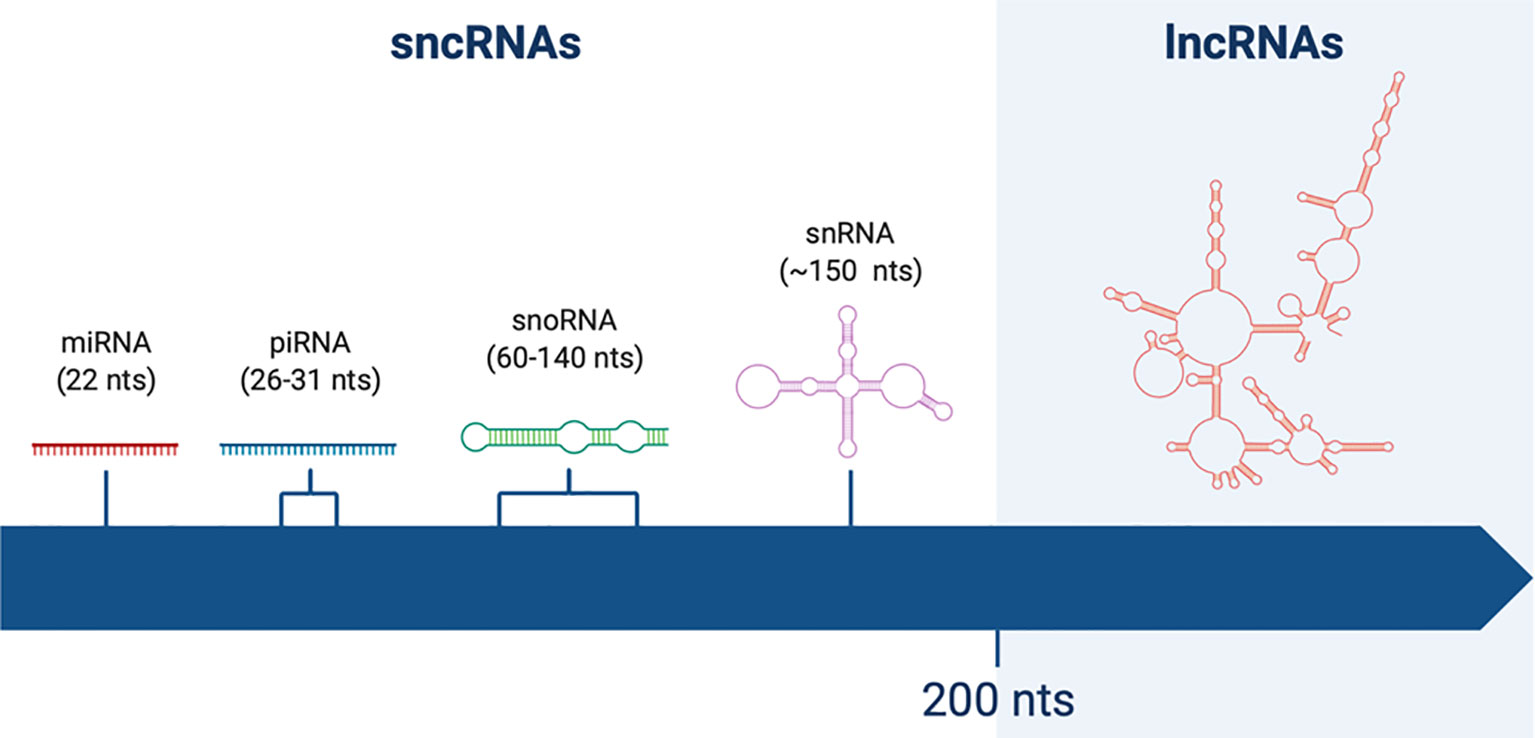
Frontiers Long Non-Coding RNAs: Role in Testicular Cancers

Each species of cancer in the human body and related gangliosides as

The transcribed-ultraconserved regions in prostate and gastric cancer: DNA hypermethylation and microRNA-associated regulation

Transcribed ultraconserved region (T-UCR) expression in human bladder

The mechanism by which transcribed ultraconserved region affects
Long non-coding RNA containing ultraconserved genomic region 8 promotes bladder cancer tumorigenesis
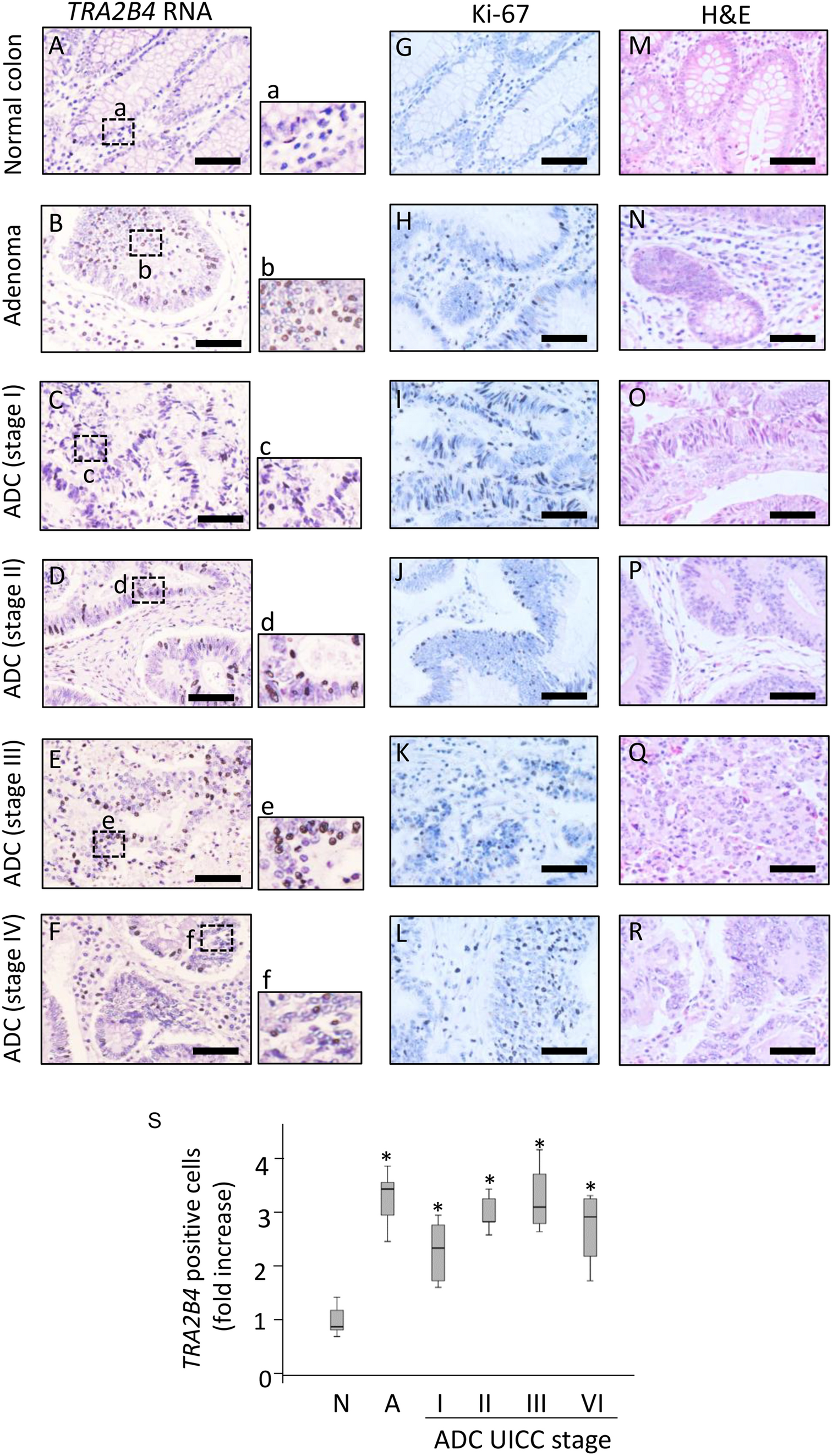
Overexpression of the transcribed ultraconserved region Uc.138 accelerates colon cancer progression
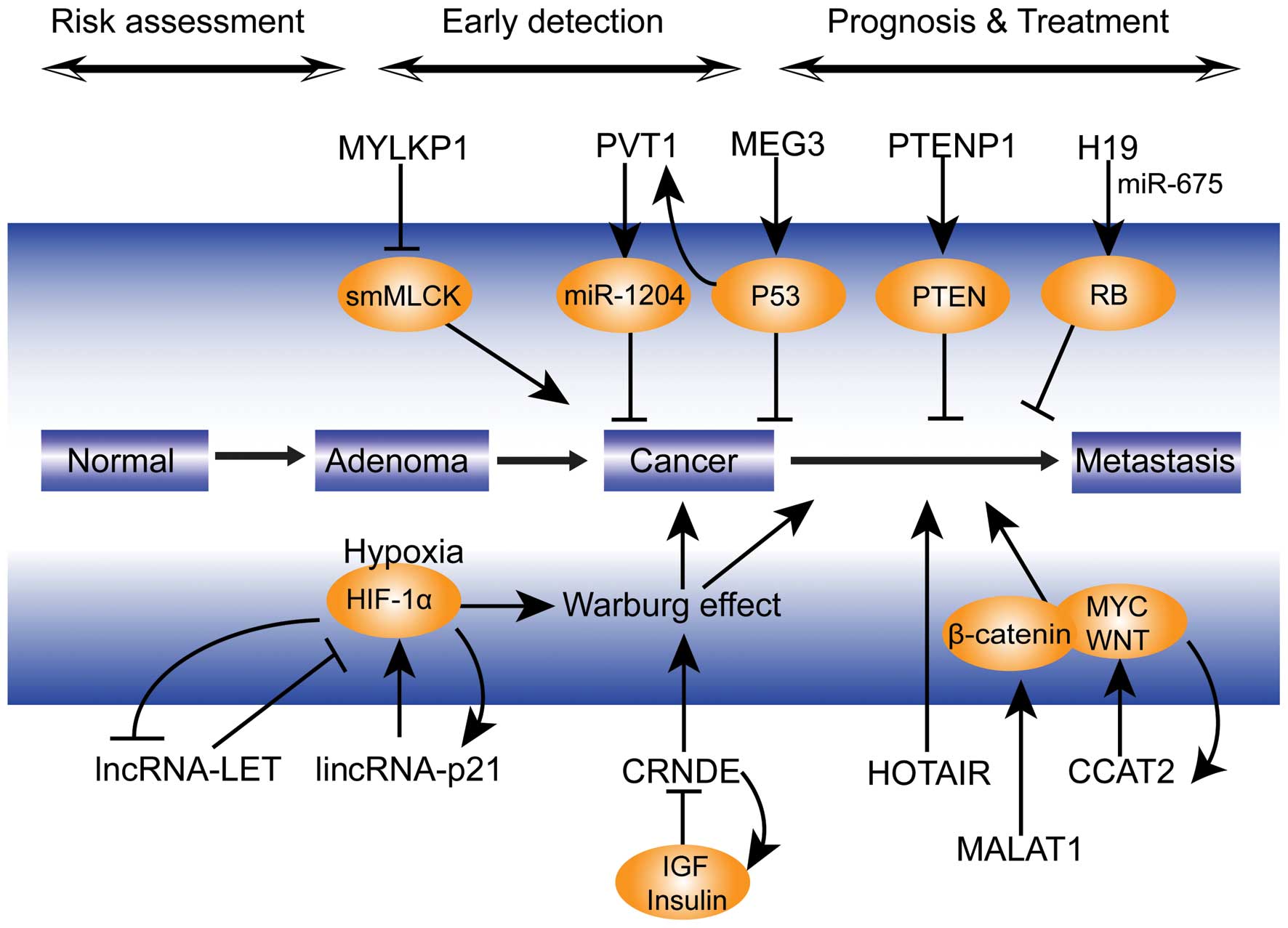
Involvement of long non-coding RNA in colorectal cancer: From benchtop to bedside (Review)







