PDF] Compressive Ulnar Neuropathies at the Elbow: I. Etiology and

The differential diagnosis of ulnar neuropathies at the elbow includes lesions that cause additional proximal or distal nerve compression and systemic metabolic disorders. &NA; Ulnar nerve compression at the elbow can occur at any of five sites that begin proximally at the arcade of Struthers and end distally where the nerve exits the flexor carpi ulnaris muscle in the forearm. Compression occurs most commonly at two sites—the epicondylar groove and the point where the nerve passes between the two heads of the flexor carpi ulnaris muscle (i.e., the true cubital tunnel). The differential diagnosis of ulnar neuropathies at the elbow includes lesions that cause additional proximal or distal nerve compression and systemic metabolic disorders. A complete history and a thorough physical examination are essential first steps in establishing a correct diagnosis. Electrodiagnostic studies may be useful, especially when the site of compression cannot be determined by physical examination, when compression may be at multiple levels, and when there are systemic and metabolic problems.

Compression Neuropathies
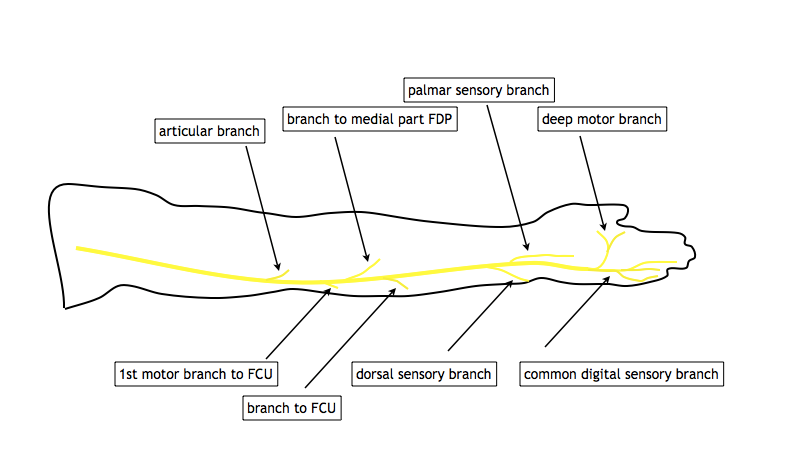
Ulnar nerve compression
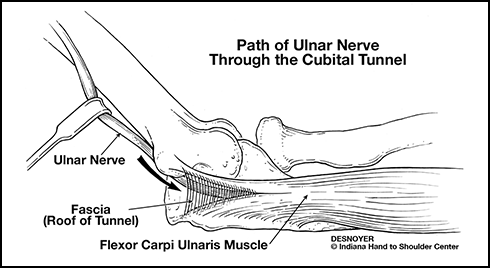
Ulnar Nerve Entrapment at the Elbow - Dr. Groh

PDF) Bilateral hypermobility of ulnar nerves at the elbow joint with unilateral left ulnar neuropathy in a computer user – A case study

Diagnosis And Treatment Of Ulnar Neuropathy At The Elbow - Cellaxys
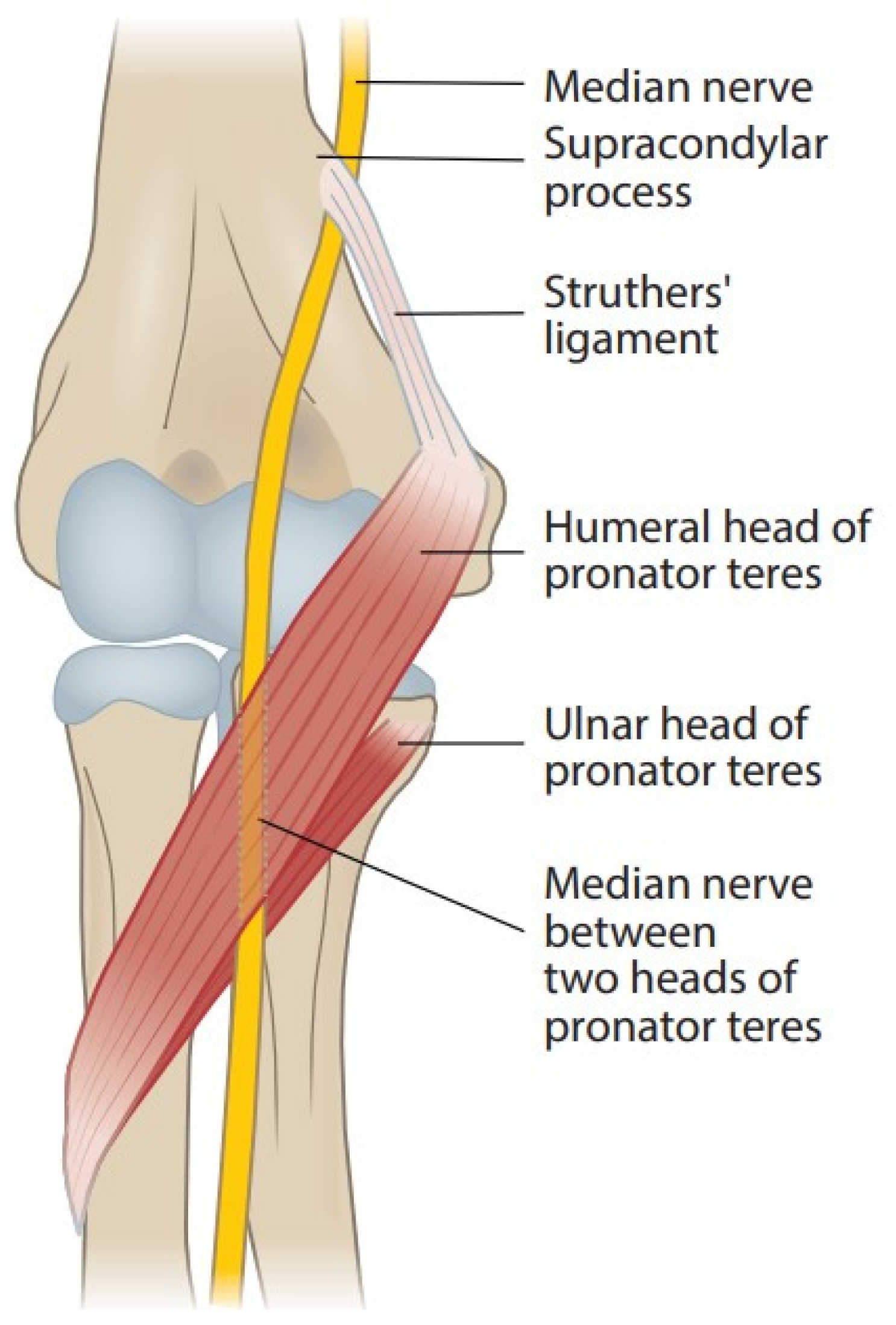
JCM, Free Full-Text

Common and uncommon nerve compression syndromes around the elbow - ScienceDirect

Cubital tunnel syndrome, Radiology Case
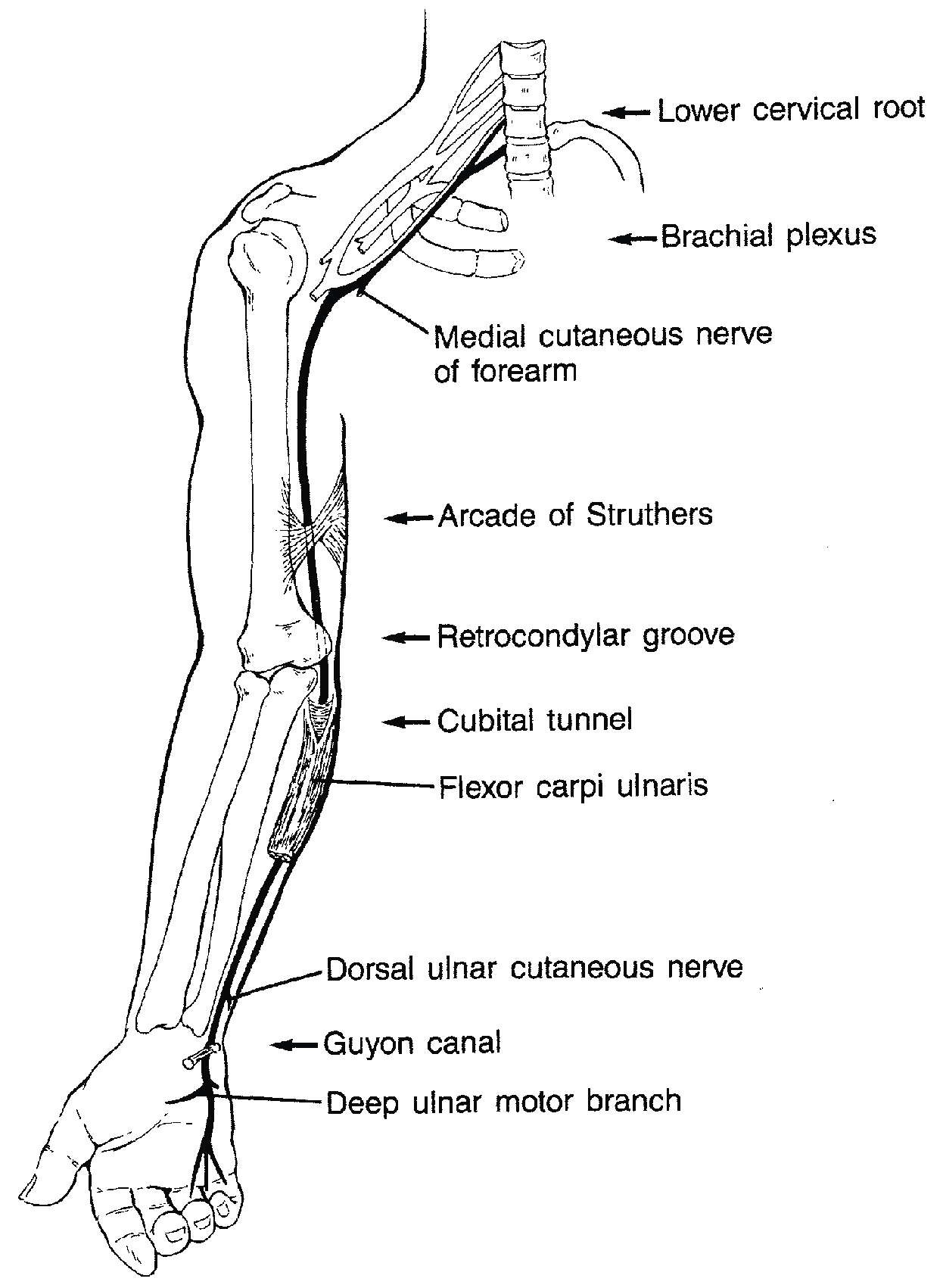
Neuropathy, ulnar (Chapter 98) - Neurologic Differential Diagnosis
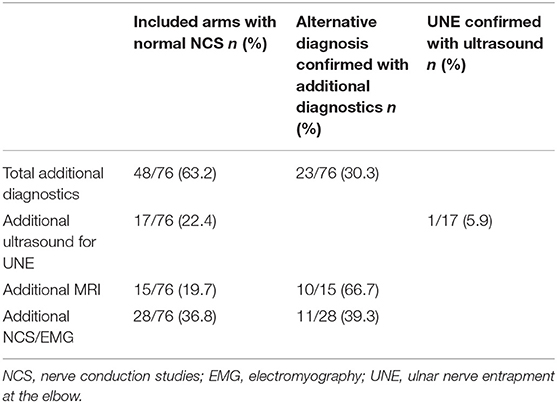
Frontiers The Diagnostic Sensitivity for Ulnar Neuropathy at the Elbow Is Not Increased by Addition of Needle EMG of ADM and FDI When Nerve Conduction Studies Are Normal
Ulnar Neuritis Information Florida Orthopaedic Institute







